In a vague attempt to steer the discussion back to where I originally intended...
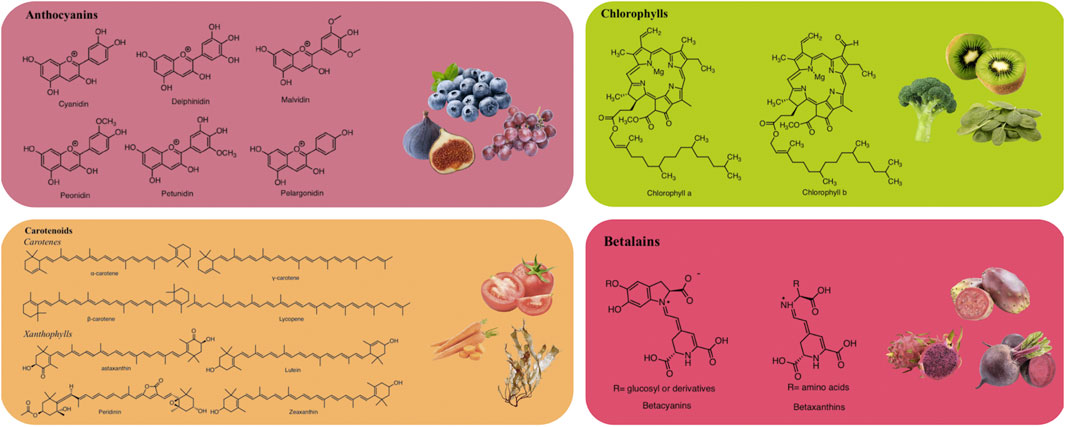
And here's some info on the four main types of plant pigments, taken from the
wikipedia page on plant pigments...
Chlorophyll is the primary pigment in plants; it is a chlorin that absorbs blue and red wavelengths of light while reflecting a majority of green. It is the presence and relative abundance of chlorophyll that gives plants their green color. All land plants and green algae possess two forms of this pigment: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Kelps, diatoms, and other photosynthetic heterokonts contain chlorophyll c instead of b, while red algae possess only chlorophyll a. All chlorophylls serve as the primary means plants use to intercept light in order to fuel photosynthesis.
Carotenoids are red, orange, or yellow tetraterpenoids. During the process of photosynthesis, they have functions in light-harvesting (as accessory pigments), in photoprotection (energy dissipation via non-photochemical quenching as well as singlet oxygen scavenging for prevention of photooxidative damage), and also serve as protein structural elements. In higher plants, they also serve as precursors to the plant hormone abscisic acid.
Betalains are red or yellow pigments. Like anthocyanins they are water-soluble, but unlike anthocyanins they are synthesized from tyrosine. This class of pigments is found only in the Caryophyllales (including cactus and amaranth), and never co-occur in plants with anthocyanins. Betalains are responsible for the deep red color of beets.
Anthocyanins (literally "flower blue") are water-soluble flavonoid pigments that appear red to blue, according to pH. They occur in all tissues of higher plants, providing color in leaves, plant stem, roots, flowers, and fruits, though not always in sufficient quantities to be noticeable. Anthocyanins are most visible in the petals of flowers of many species.[5]










